Human Element in Cybersecurity: Strengthening the First Line of Defence
Experts warn that by 2025, cyber attacks could cost the world up to $12 trillion. However, to fight back, we have powerful technology like firewalls and encryption. But there’s a key piece we often overlook — people.
Almost 95% of cyber breaches happen because of simple mistakes. That’s why teaching and empowering our employees about cybersecurity is so important. When people know how to spot and avoid risks, they add a strong layer of protection on top of our tech defenses.

In this article, we delve into the vital roles individuals play in combating cyber threats. We’ll also answer the question ‘What is vulnerability in cyber security’, and discuss the significance of fostering a cybersecurity culture at work and home. Continue reading.
The Psychology of Cyber Threats
Cybercriminals don’t just target computers; they also target the human mind. They employ a variety of underhanded techniques on the human element of cyber security to cause breaches.
But exactly what is the human element of cyber security? Well, this refers to the human behavior, decisions, and actions that significantly impact an organization’s overall security posture. It’s been estimated that 84% of cyber breaches rely on deceiving users rather than solely bypassing computer security measures. Let’s go deeper into the psychology of cyber threats.
Social Engineering Tactics
Cyber intrusions often leverage social engineering, where attackers manipulate people instead of technology. This approach deceives individuals into divulging sensitive information or unwittingly engaging in harmful actions. It uses impersonation, pretexting, and phishing to exploit human vulnerabilities in cyber security. In 2023, social engineering contributed to 43% of successful breaches, commonly through channels like emails, messages, or social media.
Leveraging Cognitive Biases
Cybercriminals exploit cognitive biases — patterns that affect decision-making to manipulate behavior. These biases include confirmation bias, where individuals seek information confirming their existing beliefs, and the availability heuristic, which affects decisions based on easily accessible data. These biases significantly impact human perception and choices.
For instance, cyber attackers might capitalize on availability bias by saturating media with reports about a specific cyber threat, causing individuals to overestimate encountering similar threats while lowering their guard against potentially more dangerous attacks. Similarly, anchoring bias can cause people to focus excessively on initial information pieces, rendering them more susceptible to manipulation through false narratives or misleading context.
To combat these tactics effectively, organizations must educate their staff about such strategies. By comprehending how cybercriminals operate, employees can recognize suspicious behavior and avoid falling into traps set by malicious actors.
Employees: The First Line of Defense
Employees are often the target of cyber attacks. However, they can also be a strong first line of defense. Well-trained employees can detect and prevent attacks before they cause harm. Studies show that companies that give their staff cybersecurity awareness training have 70% fewer data breaches.
This type of training will typically teach:
- Caution with emails and attachments from unknown sources
- Using strong passwords and keeping them private
- Use of two-factor authentication when possible
- Keeping software and systems up to date
- Reporting any suspicious activity promptly
Employee cybersecurity training offers numerous benefits:
- Reduces the risk of cyber attacks
- Increases awareness of cyber threats
- Builds trust and responsibility among employees
- Protects customer data and company secrets
- Ensures compliance with regulations and industry standards
Importance of Fostering a Cybersecurity Culture
Cybersecurity culture is the shared attitudes, behaviors, and habits in an organization relating to safeguarding digital assets and information. Establishing a cybersecurity culture centered around humans is important as it highlights the pivotal role individuals play as the primary defense against cyber attacks.
An environment where everyone understands their role in upholding security and is empowered to play an active part in it can notably boost an organization’s cyber strength as well as diminish the chances of falling victim to cyber assaults.
Here are some important elements of a human-centric cybersecurity culture.
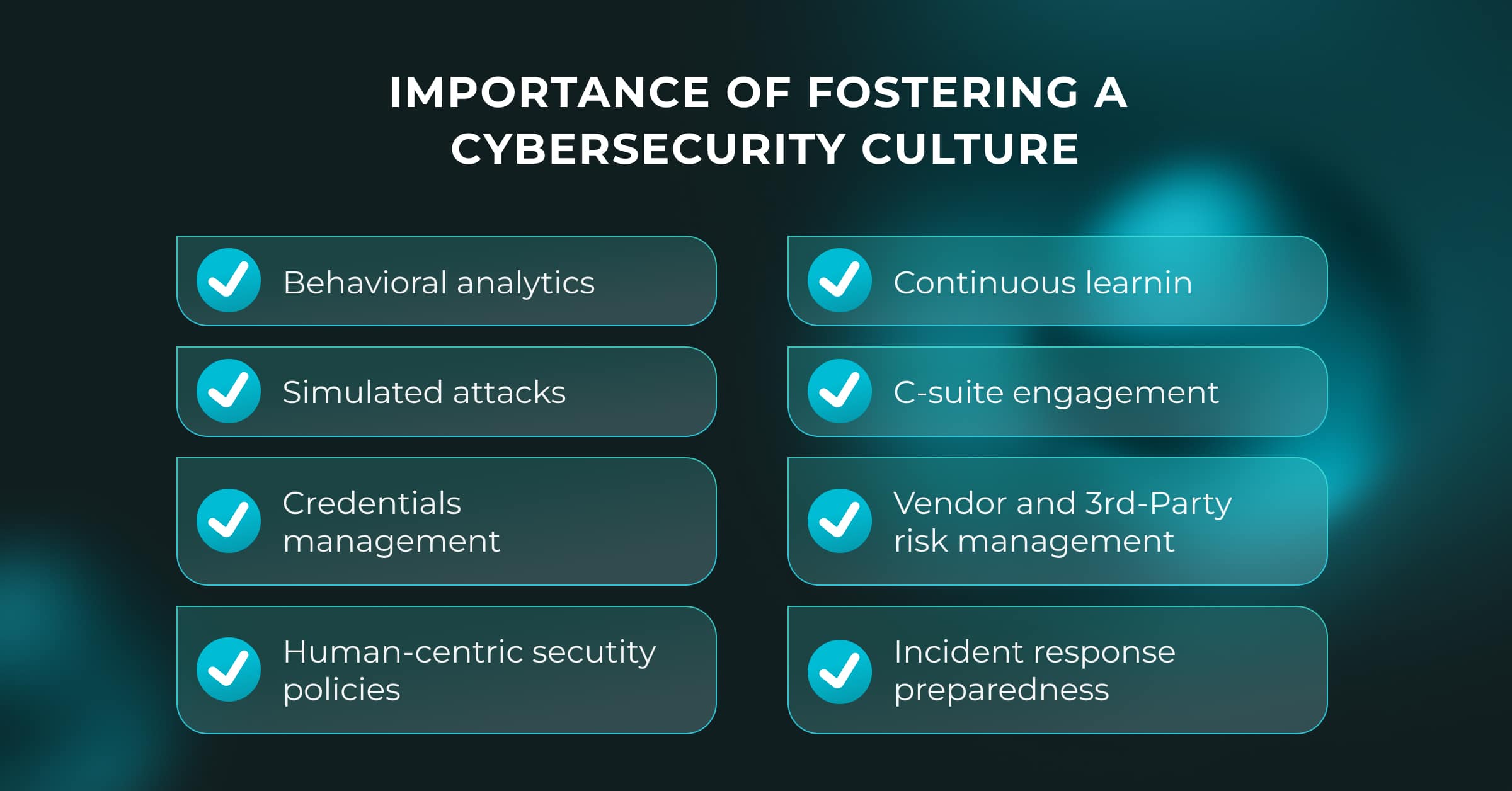
Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics is about observing and studying how people behave on a company’s network to spot any unusual patterns or activities that might suggest security problems. The idea is to learn what’s normal behavior and catch anything that looks suspicious.
For instance, if an employee usually works with certain files or apps during the day but suddenly starts accessing sensitive data late at night or from odd places, it could be a sign of a security problem like a hacked account. User Behavior Analytics (UBA) can highlight these changes so security teams can investigate and act quickly to reduce risks.
To use behavioral analytics, you need to gather and study lots of data, often with the help of machine learning. This helps find patterns and unusual behaviors effectively. By doing this, organizations can get better at spotting and dealing with security threats as they happen, making their cybersecurity stronger.
Employee Awareness and Training
A human-centric cybersecurity culture may not be possible without an investment in employee awareness and training programs. These programs are designed to enlighten employees on cyber risks and how to protect confidential data.
Training sessions may cover identifying phishing emails, creating strong passwords, securely managing sensitive information, and promptly reporting security breaches. By boosting awareness and providing employees with the requisite skills to identify and tackle potential threats, organizations can markedly reduce the likelihood of successful cyber intrusions.
Research indicates that 93% of leaders acknowledge that regular training sessions and workshops play a crucial role in reinforcing cybersecurity best practices and reducing cyber assaults. Furthermore, continuous learning opportunities and accessible resources assist in ensuring that employees stay alert and proactive in safeguarding confidential information.
Simulated Attacks
IT organizations can expand their efforts beyond education by regularly conducting simulated phishing attacks. This involves creating fake cyber attacks to test an organization’s security readiness. Ethical hackers try to breach security controls like network defenses and employee awareness to find weaknesses.
For instance, in a simulated phishing campaign, employees receive fake phishing emails to check how many fall for the scam. This helps assess the effectiveness of email filtering systems and employee training.
Regular simulated attacks help identify and fix sources of vulnerability in cyber security before real attackers exploit them. This proactive approach enhances defenses, and incident response, and safeguards sensitive data and systems from cyber threats.
Credentials Management
Managing credentials involves implementing practices and policies to handle user authentication and access credentials in an organization’s network and systems. Ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and resources effectively is essential. Effective credential management relies on implementing one or more of these key components for optimal performance.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): SSO simplifies access to multiple applications using one login, reducing the risk of weak passwords, which cause 81% of breaches. With SSO, employees log in once to access email, file sharing, and other apps without needing to re-enter credentials.
- Zero Trust Architecture: This security strategy challenges the idea of inherent trust, even within a network environment. It verifies every person and device seeking access to resources, whether inside or outside the network perimeter. For instance, employees must authenticate themselves even when accessing internal files. Zero Trust can reduce data breach costs by approximately $1 million.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA enhances security by requiring multiple verification methods—passwords, OTP, tokens, etc. This additional layer of security can prevent approximately 99.9% of automated attacks.
- Periodic Audits: Regular audits are conducted to review user permissions, access logs, and security settings for compliance purposes while also identifying unauthorized access or cyber vulnerability issues. IT departments often perform quarterly reviews to manage sensitive data access effectively.
- Account Lockout Policies: Locking accounts after several unsuccessful login attempts helps prevent brute-force attacks. For example, accounts may be temporarily locked for 15 minutes after three failed login attempts.
- Password Expiry and Rotation: Policies requiring password changes reduce the risk of attacks like credential stuffing. For example, employees may change passwords annually and can’t reuse old ones.
Human-Centric Security Policies
These policies prioritize designing security measures that enhance usability while ensuring security requirements are met. These policies aim to cultivate a security-conscious culture that effectively balances security needs with user behaviors. They avoid overly restrictive measures that impede productivity by advocating for user-friendly practices.
Continuous Learning
Continuous learning is crucial for building a strong cybersecurity culture. It means keeping employees’ skills up-to-date to match evolving cyber threats. This includes ongoing training, workshops, simulations, and resource access. Continuous learning helps cybersecurity experts develop the technical skills needed to use technologies effectively in safeguarding organizations. It also ensures staying ahead by implementing new security measures and best practices.
C-Suite Engagement
When it comes to building a cybersecurity culture centered around people, the participation of top executives is vital. C-Suite must show that they are dedicated to cybersecurity by providing direction, allocating resources, and implementing policies that promote a security-aware environment. C-Suite involvement also means encouraging open communication between leadership and staff regarding cybersecurity risks and objectives. This proactive backing from C-Suite leaders underscores the significance of security for all employees, fostering a culture of awareness and responsibility.
Vendor and Third-Party Risk Management
Third-party vendors are the cause of over 60% of data breaches. This emphasizes how crucial it is to comprehend the security concerns they might provide to a company. There are two approaches to take.
- Due Diligence: Take the time to perform in-depth evaluations before working with any vendor or service provider. This entails assessing their general dependability, regulatory compliance, and security processes.
- Continuous Monitoring: Once an offshore vendor or third party is integrated into operations, ongoing monitoring becomes vital. This practice enables organizations to track their activities and security measures over time, swiftly identifying any changes or risks that may emerge and taking timely actions to address them.
Incident Response Preparedness
Being prepared to respond effectively to cybersecurity issues is crucial. This involves establishing clear rules and practices for detecting, containing, and promptly resolving security breaches or events. Additionally, it requires regular staff training and exercises to ensure they comprehend their roles and responsibilities during an incident. It’s also essential to have technological tools and resources readily available to support incident response activities.
Human actions, whether inadvertent or intentional, greatly affect an organization’s security, so it’s crucial to have a strategy that revolves around the people in your organization. This means not only tightening digital loopholes but also empowering and educating staff to identify, address, and handle cyber risks as they evolve.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Prioritizing the Human Element
As cyber threats evolve, it is clear that relying solely on traditional security measures will no longer be sufficient. The future depends on prioritizing the human element of cyber security. Here are some key trends to watch out for:
Artificial Intelligence, Automation and Machine Learning
As threats grow in complexity, one of the key trends of 2024 and beyond is the reliance on AI, ML, and automation to strengthen cybersecurity teams. These techs can help humans detect and address threats, and automate mundane tasks. The marriage between humans and AI/ML will help bolster cybersecurity defenses and help organizations effectively protect their digital assets.
Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics is pivotal in cybersecurity, delving into individual behaviors to spot threats. By scrutinizing data from diverse resources like network logs and user activities, this method can pinpoint anomalies and predict threats in advance. This technology holds great promise in bolstering cybersecurity defenses, allowing companies to keep pace with evolving threats.
IT Staff Augmentation
The importance of specialized expertise to manage network infrastructures cannot be overemphasized. This is where IT staff augmentation comes in, to offer specialized insights, bridge talent gaps, encourage diversity, and improve cybersecurity readiness. From incident response to threat detection, this approach will make it easy for companies to proactively respond to emerging threats. According to Kaspersky, tapping into outside expertise can be 24% more important in preventing cyber security breaches.
Conclusion
While technological advancements continue to shape defense strategies, the importance of skilled professionals cannot be overstated. Investing in the development and augmentation of employees — transforming them from weak links into efficient defense is a strategic imperative to succeed in the cybersecurity war. If you’re seeking specialized expertise, Newxel can assist.
Our IT staff augmentation services can bolster your cybersecurity team with the right talents, strengthening your defense against cyber threats. Build a team that comes with the relevant expertise and resources needed to strengthen your cybersecurity efforts today.